Essay Prompt: Explain the Procedure of Infection of this Virus
How does this virus spread?
What classifies organisms as living?
Are viruses alive?
What makes up a virus?
How do viruses replicate?
What are some examples of viruses?
Viruses are not considered living because they do not meet these characteristics...but once in a host they hijack the its machinery to create more of the virus.
Many viruses have a similar composition of protein and nucelic acid. (some have a lipid coat)
A viruses can replicate using 2 cycle processes:
Lytic Cycle where the cell bursts, killing the host cell.
Lysogenic Cycle where the viral DNA is integrated into the host DNA. External factors (stress conditions) may trigger the virus into going into the Lytic Cycle.
What are some examples of viruses?
Ebola: fatality rate of up to 90%, the Ebola Virus Disease (also called Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever) is believed to be one of the deadliest virus infection all over the world.
Rabies Virus: causes 55,000 human deaths each year, if left untreated 100% fatality rate.
Smallpox Virus: very few deaths due to a vaccine but if patients contract the virus 90% fatality rate .
Chickenpox Virus: (varicella) used to be very common in the United States before the chickenpox vaccine became available in 1995. In the early 1990s, an average of 4 million people got chickenpox, 10,500 to 13,000 were hospitalized (range, 8,000 to 18,000), and 100 to 150 died each year.
HIV: this virus has claimed the lives of millions. In many cases if no treatment/medication 100% fatality.
SARS: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome about 10% fatality rate.
Viroids: nucleic acid molecule that infects plants
Prions: protein molecule that infects the hosts neurological system
Mad Cow Disease
Zika virus
Are you controlled by viruses
Prions: protein molecule that infects the hosts neurological system
Mad Cow Disease
Zika virus
Are you controlled by viruses
Prokaryotes
Characteristics:
- no membrane bound organelles
- free floating DNA in circular form and/or a plasmid (separate part of DNA)
- unicellular
- motile (movement) by use of flagella and/or pili
Groups of Prokaryotes
- Obligate anaerobes can not survive in the presence of O2
- Obligate aerobes must have O2 to survive
- Facultative aerobes are can survive in the presence or absence of O2.
Archaebacteria vary in shapes and live in extreme environments
There are 3 types of structures of Eubacteria.
Rod shape - Bacilli
Spiral shape - Spirilla
Spherical shape - Cocci
Reproduction/Conjugation
Bacteria reproduce sexually using their pili

They can also reproduce asexually through BINARY FISSION.
Gram Staining
Gram Negative Bacteria have the extra layer of protection which makes them harder to treat. Their cell walls are resistant to several classes of antibiotics.
Benefits/Treatments
Some bacteria inside our bodies are beneficial. They help organisms breakdown food. Some make vitamins and other compounds.
They have a mutualistic symbiosis with organisms. Bacteria breakdown food and keep them healthy, while organisms protect them.
Bacteria can be treated with Antibiotics.
EXAMPLES
E.coli & Salmonella= cause food poisoning
H.Pylori= cause ulcers and gastritis

Staphylococcus aureus= causes a variety of infections in the body, including boils, cellulitis, abscesses, wound infections, toxic shock syndrome, pneumonia, and food poisoning
Streptococcus pyogenes = strept throat
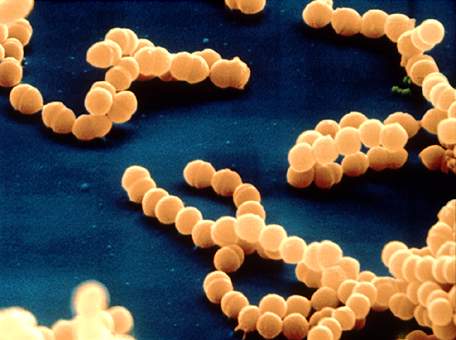
Nactrotizing fasciitis = Flesh eating bacteria
Leprocy